-
Products
Overview Products
-
2D Cutting
-
Tube Cutting
-
3D Cutting
-
Intelligent Welding
-
Intelligent Cutting Head
-
Industrial Automation
-
Industrial Software
-
Combination
-
Combination
BOCHU New Product -
Combination
BOCHU New Product -
Controller
BOCHU New Product -
2D Cutting Head
Tube Cutting Head
3D Cutting Head
Consumables
BOCHU New Product -
Servo
BOCHU New Product -
Industrial 4.0
-
- Support
- About
- Online Store

- Software Download
- Manual
- Video
- Tutorial
I. Introduction
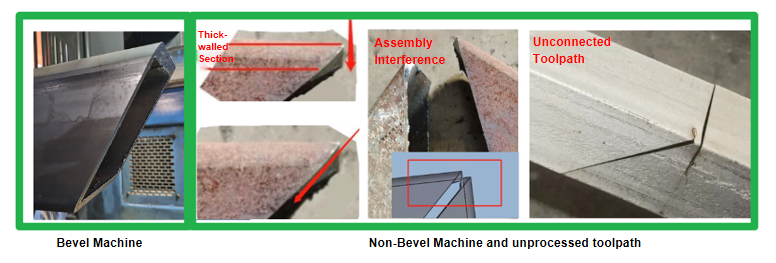
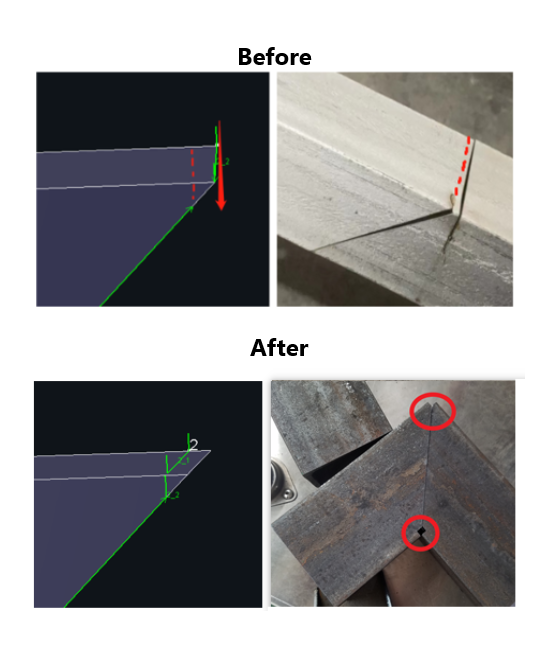
When the cutting machine is not a beveling model, the cutting head cannot tilt and always emits the laser vertically. As a result, it is unable to create bevels on the wall thickness of the tube.
For rectangular tubes and one-pass cutting of channel steel or angle iron, joint interference may occur during assembly.
For channel steel or angle iron using segmented cutting, due to the presence of wall thickness gaps, not only can joint interference occur, but there may also be issues with toolpath discontinuity.
II. Solution
For this kind of problem, there are two solutions:
Note: 《》, 【】 in blue font are jumpable tutorial links, click the link, you can view the function corresponding to the detailed parameters of the description, use.
| Solution | Applicable Tube Type | Cautiou |
|
Use 【 Weld Kerf 】 |
Under the premise of drawing standards Except for I-beams there is no restriction on pipe type and angle for the time being. |
①There will be welding gap after compensation, you can fill the welding liquid. ② National standard channel steel (i.e., hot rolled, channel steel with internal R angle) is not supported for the time being, and the toolpath should be carefully after setting. |
|
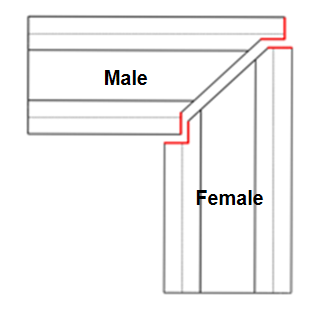
Use【Male-Female Joint】 |
Can be used for rectangular tubes, channel steel | Recommended for 45° miter cuts (i.e. L-shaped splices) |
I. Introduction
When the cutting machine is not a beveling model, the cutting head cannot tilt and always emits the laser vertically. As a result, it is unable to create bevels on the wall thickness of the tube.
For rectangular tubes and one-pass cutting of channel steel or angle iron, joint interference may occur during assembly.
For channel steel or angle iron using segmented cutting, due to the presence of wall thickness gaps, not only can joint interference occur, but there may also be issues with toolpath discontinuity.
II. Solution
For this kind of problem, there are two solutions:
Note: 《》, 【】 in blue font are jumpable tutorial links, click the link, you can view the function corresponding to the detailed parameters of the description, use.
| Solution | Applicable Tube Type | Cautiou |
|
Use 【 Weld Kerf 】 |
Under the premise of drawing standards Except for I-beams there is no restriction on pipe type and angle for the time being. |
①There will be welding gap after compensation, you can fill the welding liquid. ② National standard channel steel (i.e., hot rolled, channel steel with internal R angle) is not supported for the time being, and the toolpath should be carefully after setting. |
|
Use【Male-Female Joint】 |
Can be used for rectangular tubes, channel steel | Recommended for 45° miter cuts (i.e. L-shaped splices) |